Title
What is geothermal energy?
Geothermal comes from natural heat stored beneath Earth’s surface. The term “geothermal” combines “geo” – earth – and “thermal” – heat. This renewable energy source can be used to generate electricity, heat buildings, and provide hot water. The Earth’s crust contains an abundance of energy. The first 10 kilometers hold around 50,000 times more energy than all the world’s oil and natural gas combined. Although geothermal currently provides about 1% of the U.S energy supply, it has the potential to meet 10% of the natural electricity demand by 2050 with more investment and technological innovation.
There are three levels of geothermal available: Power plants, community-scale, and residential heat pumps.
Geothermal energy provides a variety of benefits, including low emissions, minimal land use, and low environmental impact. It is available 24/7 and is not impacted by changes in the weather. This makes it incredibly efficient and reliable. The small amount of solid waste generated from geothermal plants, such as sulfur, can often be reused or reprocessed.
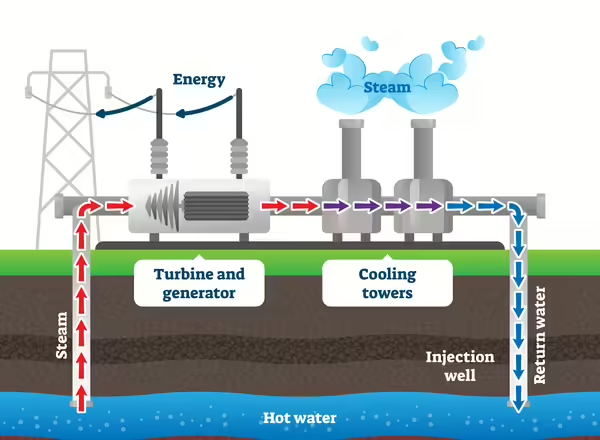
Geothermal energy is available at three scales: Utility, district, and residential. At the largest scale, geothermal power plants generate electricity by tapping into underground reservoirs of steam or hot water. The heat brought to the surface drives turbines, producing electricity. The water is then returned underground to be reheated and reused, creating a sustainable loop.
Title
Geothermal Power Plants
There are three main types of geothermal power plant technologies:
- Dry steam: This is the oldest and most common, and it uses steam directly from underground to turn turbines.
- Flash steam: Brings hot water to the surface and rapidly depressurizes it to produce steam.
- Binary cycle: Uses moderately hot water to heat another liquid to a lower boiling point, which turns into vapor and spins the turbine.
In places like Northern California, geothermal power plants play a significant role, supplying almost 60% of their energy needs. This area contains the world’s largest geothermal field, spanning 30 square miles with 18 power stations and 1,517 MW installed capacity. It produces 20% of California’s renewable energy.
Until recently, geothermal power plants were limited to locations with natural features like hot springs. However, advancements in technology now allow plants to be in more parts of the country. While Illinois doesn’t currently have geothermal power plants, the state is still generating geothermal energy at the community and residential scale for heating and cooling.
Title
Community-Scale Geothermal Systems
District geothermal systems, also known as community-scale systems, heat and cool multiple buildings through a shared underground loop network. These systems use geothermal heat pumps to move heat between the ground and buildings via a central energy station. The system adjusts with the seasons:
- In winter, it pulls heat from the ground into buildings.
- In summer, it reverses the process, moving heat from buildings into cooler ground.
District systems are efficient and reliable, making them ideal for neighborhoods, campuses, and downtowns. Through the Community Geothermal Heating and Cooling Initiative, community-scale geothermal heating and cooling systems will be installed in the West Woodlawn neighborhood in the Southside of Chicago. This project, led by Blacks in Green, will use the alleyways to install the geothermal system. A major roadblock with geothermal installation like this can be a lack of workable space; however, since there is nothing currently installed underneath the alleys, it makes them a perfect place to install the system. Once complete, it will provide heating and cooling, and lower utility bills for potentially more than 200 households.
Title
Residential Geothermal Heat Pumps
Geothermal heat pumps, also known as ground-source or water-source heat pumps, use the stable temperature of the shallow earth, typically 40°F to 70°F, to heat and cool buildings. These systems work anywhere the ground can be accessed below the depth affected by seasonal temperature changes. By tapping into this consistent heat source, geothermal heat pumps offer:
- Year-round energy efficiency, providing heating and cooling 24/7, 365 days a year, regardless of weather conditions
- Up to 50% savings on energy costs compared to conventional systems
- Quiet operation with no combustion or outdoor units, reducing safety concerns
- Long lifespan: Indoor components can last 20–25 years, while the underground loop system can last 50 years or more
Installation costs for these systems are higher, but they pay for themselves over time. There are incentives and rebates offered through utilities and tax credits that can reduce costs. Installation costs can range from $10,000 to $40,000, with an average system for a 2,000-square-foot home costing up to $30,000. Many homeowners recover the expense in 4 to 15 years through energy savings, especially if they plan to stay in the home long-term. If you're building a new home, geothermal can be more cost-effective to install from the start. For existing homes, the benefits add up the longer you stay.